
6082 vs 6061 Aluminum Forging Key Differences Explained

6082 and 6061 aluminum alloys stand out as popular choices for forging. Each alloy offers unique advantages in strength, machinability, corrosion resistance, and cost. The table below summarizes their main differences:
Property | 6082 Aluminum Alloy | 6061 Aluminum Alloy |
|---|---|---|
Strength | Higher strength, suitable for load-bearing | Good strength, but lower than 6082 |
Machinability | More challenging due to higher strength | Easier to machine with standard tools |
Corrosion Resistance | Better resistance, especially in high-moisture environments | Good resistance, especially after welding |
Cost | Generally more expensive | Less expensive, more cost-effective |
Selecting the right alloy depends on project requirements. Engineers should consider whether high strength or easy machinability matters most for their application. 6082 Aluminum Forging suits heavy-duty needs, while 6061 works well for versatile tasks.
Quick Comparison
6061 vs 6082 Overview
Engineers often compare 6061 vs 6082 aluminum alloys when selecting materials for forging projects. Both alloys offer distinct advantages in mechanical properties and typical uses. The following table highlights the main differences between these two popular choices:
Property | 6061 Aluminum Alloy | 6082 Aluminum Alloy |
|---|---|---|
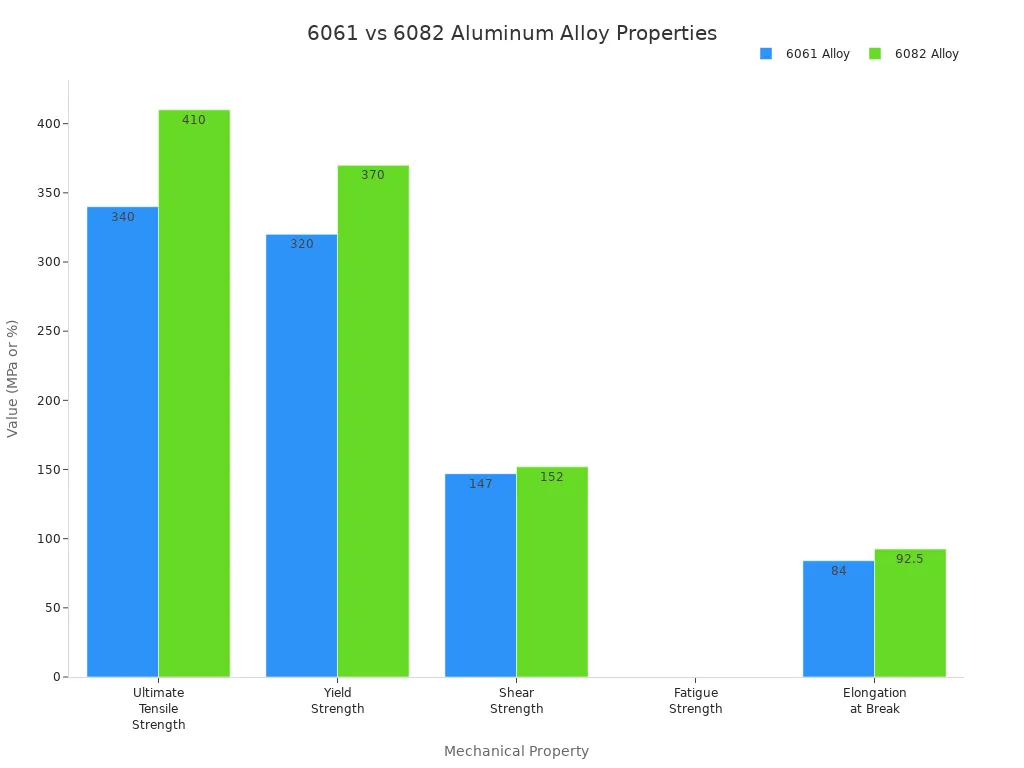
Ultimate Tensile Strength | 340 MPa | 410 MPa |
Yield Strength | 320 MPa | 370 MPa |
Shear Strength | 84–210 MPa | 84–220 MPa |
Fatigue Strength | 58–110 MPa | 55–130 MPa |
Elongation at Break | 3.4% to 20% | 6.3% to 18% |
6061 vs 6082 alloys serve different industries. 6061 aluminum appears in aerospace components, bicycle frames, marine structures, industrial equipment, and furniture profiles. 6082 aluminum finds use in bridge structures, cranes, rail vehicle frames, and offshore platform components.
Key Differences
The 6061 vs 6082 comparison reveals several key distinctions. 6082 aluminum provides higher strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. 6061 aluminum offers easier machinability, which benefits projects that require complex shapes or precise cuts. Corrosion resistance favors 6082, especially in harsh or high-moisture environments. Cost also plays a role; 6061 aluminum usually costs less and is more widely available.
Tip: When choosing between 6061 vs 6082, consider the demands of the project. Heavy machinery and structural beams often require the strength of 6082. Aircraft parts, marine equipment, and automotive components benefit from the versatility and machinability of 6061.
The following list summarizes typical uses for each alloy:
6061 aluminum alloy:
Aircraft parts
Marine equipment
Automotive components
Structural components
6082 aluminum alloy:
Construction
Heavy machinery
Structural beams
Machine parts
Frames
The 6061 vs 6082 debate centers on matching alloy properties to project needs. Strength, machinability, corrosion resistance, and cost all influence the final decision.
Chemical Composition

6082 Aluminum Forging Elements
6082 aluminum contains several key alloying elements that shape its properties. The main elements include silicon, magnesium, manganese, iron, and chromium. Silicon improves fluidity during casting and forms a hard compound with magnesium, which strengthens the alloy. Magnesium and silicon together create magnesium silicide, a compound that plays a crucial role in both strength and corrosion resistance. Manganese stands out in 6082 aluminum. This element refines the grain structure and helps counteract the negative effects of iron, which often appears as an impurity. Iron, when present in small amounts, can boost strength but may reduce ductility if levels rise too high.
Note: Manganese content in 6082 aluminum is higher than in many other alloys. This addition controls the grain structure, resulting in a stronger and tougher alloy.
Element | Role in 6082 Aluminum |
|---|---|
Silicon | Enhances fluidity, forms hard compounds |
Magnesium | Increases strength, improves corrosion resistance |
Manganese | Refines grain structure, boosts strength |
Iron | Adds strength in small amounts, reduces ductility if excessive |
Chromium | Supports mechanical strength |
The combination of these elements gives 6082 aluminum its reputation for high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, especially in demanding environments.
6061 Aluminum Elements
6061 aluminum uses a different balance of alloying elements. Each element contributes to the alloy’s machinability, ductility, and overall performance:
Silicon: Improves strength, corrosion resistance, and castability.
Copper: Raises strength but can lower ductility and machinability if present in large amounts.
Zinc: May enhance strength but can reduce corrosion resistance.
Chromium, manganese, and iron: Support mechanical strength and machinability.
6061 aluminum’s composition makes it easy to machine and shape. The alloy maintains good strength and corrosion resistance, which explains its popularity in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. The careful selection of elements ensures that 6061 aluminum remains versatile and reliable for a wide range of forging applications.
Mechanical Properties
6061 T6 vs 6082 T6 Strength
Engineers often compare 6061 t6 vs 6082 t6 when selecting a higher strength alloy for demanding projects. Both alloys deliver impressive mechanical strength, but their performance differs in key areas. The 6061 t6 vs 6082 t6 debate centers on tensile strength, yield strength, and overall durability.
6082 T6 tensile strength: Minimum 295 N/mm²
6082 T6 yield strength: Minimum 255 N/mm²
6082 T6 elongation on 50mm: Minimum 8%
6061 t6 vs 6082 t6 shows that 6082 T6 stands out as the higher strength alloy. This material handles heavy loads and resists deformation under stress. The yield strength of 6082 T6 supports structural integrity in bridges and machinery. In contrast, 6061 T6 offers good tensile strength and yield strength, but it does not match the strength of 6082 T6. Many industries choose 6061 t6 vs 6082 t6 based on the need for strength in critical components.
When selecting between 6061 t6 vs 6082 t6, engineers should prioritize strength for load-bearing applications. 6082 T6 provides a higher strength alloy for demanding environments.
Ductility and Hardness
The mechanical properties of 6061 t6 vs 6082 t6 also include ductility and hardness. 6061 T6 demonstrates greater ductility, allowing it to bend and shape without cracking. This property makes 6061 T6 suitable for parts that require forming or machining. The hardness of 6082 T6 increases with heat treatment, but its ductility remains lower than 6061 T6.
Material datasheets reveal that elongation percentages change with heat treatment. For example, 6082 T6 shows a significant increase in elongation after exposure to high temperatures. At 500 °C, the percentage elongation after fracture rises nearly twofold compared to untreated specimens. This variability highlights the importance of considering mechanical strength and ductility when choosing between 6061 t6 vs 6082 t6.
6061 t6 vs 6082 t6 comparisons show that 6082 T6 excels in strength, while 6061 T6 offers better ductility. Engineers must weigh these factors when selecting the right alloy for their project.
Machinability & Workability
6061 Aluminum Machinability
6061 aluminum stands out for its excellent machinability. Manufacturers often choose this alloy for projects that require precise cuts and complex shapes. The alloy responds well to standard machining tools, which helps reduce production time and tool wear. Many industries rely on 6061 aluminum for its versatility in both manual and automated machining processes.
The machinability ratings for these alloys show their performance in real-world applications:
Alloy | Machinability Rating |
|---|---|
6061 | |
6082 | 270% |
Both 6061 aluminum and 6082 aluminum share the same machinability rating. However, 6061 aluminum remains easier to machine because of its lower hardness. This property allows for faster production and smoother finishes. Engineers often select 6061 aluminum for parts that need tight tolerances or intricate designs.
Tip: 6061 aluminum offers excellent machinability, making it a top choice for components that require frequent modifications or detailed features.
Forging with 6082
Forging with 6082 aluminum presents unique challenges and benefits. The alloy’s higher strength and hardness make it more difficult to machine compared to 6061 aluminum. Production times may increase, and tools can wear out faster. Despite these challenges, 6082 aluminum delivers superior strength and durability in the final product.
Characteristic | 6061 Aluminum Alloy | 6082 Aluminum Alloy |
|---|---|---|
Machinability | Excellent machinability and versatility | More challenging to machine due to hardness |
Process Efficiency | Faster production times, less tool wear | Slower production due to increased hardness |
Final Product Quality | Versatile, suitable for various applications | Superior strength and durability for high-stress applications |
Corrosion Resistance | Moderate corrosion resistance | Better corrosion resistance in harsh environments |
6061 aluminum is versatile and easy to work with, ideal for applications requiring good machinability.
6082 aluminum offers higher strength and better corrosion resistance, suitable for high-stress applications.
The choice between these alloys depends on the balance between ease of processing and the desired mechanical properties.
Weldability
6061 vs 6082 Welding
Weldability plays a crucial role when choosing between 6061 and 6082 aluminum alloys. 6061 aluminum stands out for its ease of welding and higher ductility. This alloy maintains more of its original strength after welding. Many industries, such as aerospace and automotive, prefer 6061 for projects that require extensive welding. The alloy’s structure allows it to handle the heat of welding without losing significant mechanical properties.
In contrast, 6082 aluminum presents more challenges during welding. Its higher manganese content can cause a loss of strength in the heat-affected zones. This reduction in strength makes 6082 less suitable for applications where welded joints must bear heavy loads. The alloy’s lower ductility also increases the risk of cracking during and after welding.
Note: 6061 aluminum is often the first choice for welded structures that demand both strength and reliability.
Key points to remember:
6082 aluminum may lose strength in welded areas.
6061 is more ductile, reducing the risk of cracking.
Best Practices
Welding experts recommend specific techniques to achieve the best results with these alloys. For 6061 aluminum, Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding offers precise control over heat input. This method helps prevent overheating and ensures a clean weld. Pre-heating the material can further reduce the risk of cracking and improve fusion, though it is not always required.
To minimize warping and distortion, welders should use uniform preheating, apply minimal heat, and secure the workpiece with fixtures. Choosing the right filler material is also important. For 6061 aluminum, ER4043 and ER5356 fillers provide strong, compatible welds.
Recommended welding techniques:
TIG welding for precise heat control
Pre-heating to prevent cracking
Use of ER4043 or ER5356 filler rods
Fixtures to hold parts steady and reduce warping
By following these best practices, welders can achieve strong, reliable joints in both 6061 and 6082 aluminum, though 6061 remains the easier and more forgiving option.
Corrosion Resistance
6082 Aluminum Forging in Harsh Environments
6082 aluminum stands out for its better corrosion resistance, especially in harsh and demanding environments. Many engineers choose this alloy for marine and industrial applications. The magnesium and manganese in its composition work together to protect the metal from saltwater and moisture. This combination helps prevent rust and surface damage, even when exposed to aggressive chemicals or outdoor conditions.
6082 aluminum alloy shows better corrosion resistance in marine environments.
Magnesium and manganese improve its ability to resist saltwater corrosion.
The alloy performs well in industrial machinery and outdoor equipment.
These features make 6082 a top choice for structures that face constant exposure to water or chemicals. Bridge components, ship parts, and offshore platforms often use 6082 because of its better corrosion resistance. The alloy’s durability helps reduce maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of forged parts.
6061 Aluminum Protection
6061 aluminum also offers good corrosion resistance, but it does not match the level seen in 6082. This alloy works well for many general-purpose applications. After welding, 6061 maintains its protective oxide layer, which shields the metal from moisture and air. However, in severe marine or industrial environments, 6061 may require extra coatings or treatments to achieve better corrosion resistance.
Engineers often select 6061 for projects where moderate corrosion resistance is enough. Furniture, bicycle frames, and automotive parts benefit from its balance of strength and protection. When comparing corrosion resistance differences, 6082 clearly provides better corrosion resistance in the most challenging settings.
Tip: For projects in saltwater or chemical-rich environments, 6082 aluminum forging delivers better corrosion resistance and longer service life than 6061.
Cost & Availability
Price Comparison
Manufacturers often consider the price when selecting between 6061 and 6082 aluminum alloys. The price differences between these two materials can influence project budgets and material choices. In 2024, the average market price for 6061 aluminum alloy ranges from $1.8 to $3.0 per kilogram. The price for 6082 aluminum alloy is higher, typically between $4.30 and $4.75 per kilogram. This gap reflects the increased strength and corrosion resistance found in 6082 aluminum.
Alloy | Price Range (USD/kg) |
|---|---|
6061 | |
6082 | $4.30 – $4.75 |
Engineers see that the price for 6082 aluminum alloy varies by product form. For example:
Sheet: $4.30 per kg
Plate: $4.60 per kg
Tube: $4.75 per kg
Bars: $4.65 per kg
The higher price for 6082 aluminum often leads buyers to choose 6061 aluminum for cost-sensitive projects. The price differences become more important for large-scale orders or applications where material costs make up a significant part of the budget.
Note: 6061 aluminum alloy offers a lower price and remains a popular choice for projects that do not require the highest strength or corrosion resistance.
Market Access
6061 aluminum alloy is widely available in global markets. Suppliers stock this alloy in many forms, including sheets, plates, tubes, and bars. The lower price and broad availability make 6061 aluminum a practical option for many industries. 6082 aluminum alloy, while available, may require special orders for certain sizes or shapes. The higher price and limited market access can affect lead times and overall project costs.
Manufacturers often select 6061 aluminum for its easy sourcing and competitive price. 6082 aluminum serves specialized needs, especially where strength and corrosion resistance justify the higher price. Buyers should check local suppliers for current price and availability before making a final decision.
Applications

6082 Aluminum Forging Uses
Engineers select 6082 aluminum alloy for projects that demand high strength and durability. This alloy performs well in heavy-duty structural applications. In the automotive industry, manufacturers use 6082 aluminum forgings for car body frames, door frames, roof bends, and body reinforcements. Engine components such as crankcases, cylinder heads, and connecting rods also benefit from its strength. Suspension system parts, including suspension arms and shock absorber seats, rely on 6082 for stability and handling. Brake system components like brake calipers and drums require materials that withstand high temperatures and pressure, making 6082 a preferred choice. Automobile wheels made from this alloy improve suspension response and fuel efficiency.
In aerospace, 6082 aluminum forgings serve as crucial structural components. The high tensile and yield strength ensure safety and performance in demanding environments. Offshore platforms, bridge structures, and cranes also use this alloy for its ability to resist corrosion and maintain integrity under stress.
Component Type | Applications |
|---|---|
Car Body Structural Parts | Body frames, door frames, roof bends, reinforcements |
Engine Components | Crankcases, cylinder heads, connecting rods |
Suspension System Components | Suspension arms, rods, shock absorber seats |
Brake System Components | Brake calipers, brake drums |
Automobile Wheels | Lightweight, strong wheels |
6082 aluminum alloy provides high strength and stiffness, making it ideal for stable suspension performance and durable brake systems. The applications of 6082 aluminum alloy focus on environments where reliability and strength are essential.
6061 Aluminum Uses
6061 aluminum alloy stands out for its versatility and machinability. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, marine, and consumer goods rely on this alloy for a wide range of products. Aircraft components and structural parts benefit from its balance of strength and ease of fabrication. Automotive manufacturers use 6061 for vehicle frames, parts, and accessories. Construction projects incorporate this alloy into building materials and scaffolding. Marine applications include boat hulls and fittings, where corrosion resistance is important. Furniture and sporting goods represent common consumer products made from 6061 aluminum.
Industry | Typical Products |
|---|---|
Luft-und Raumfahrt | Aircraft components, structural parts |
Automotive | Vehicle frames, parts, accessories |
Construction | Building materials, scaffolding |
Marine | Boat hulls, fittings |
Consumer Goods | Furniture, sporting goods |
Luft-und Raumfahrt
Automotive
Construction
Marine
Consumer Goods
The applications of 6061 aluminum alloy extend to projects that require easy machining and reliable performance. Manufacturers choose this alloy for its adaptability and cost-effectiveness.
Which to Choose?
6061 vs 6082 Decision Guide
Selecting the right aluminum alloy for forging projects depends on several important factors to consider. Engineers and designers must weigh project priorities such as strength, machinability, corrosion resistance, cost, and environmental exposure. The following guide helps match alloy properties to common use cases, making the decision process straightforward.
Quick Comparison Table
Property | Aluminum Alloy 6061 | 6082 Aluminum Alloy |
|---|---|---|
Strength | Good | Higher |
Machinability | Excellent | Good |
Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
Weldability | High | Moderate |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Environmental Exposure | Atmospheric | Marine, Chemical |
Typical Applications | Aerospace, Construction | Transportation, Heavy Duty |
Decision Criteria for High-Strength Applications
6082 aluminum alloy provides about 10-12% higher tensile strength than aluminum alloy 6061.
For structural applications that demand high strength and good weldability, 6082 stands out as the preferred choice.
The T6 heat-treated condition of 6082 enhances its hardness and strength, making it suitable for demanding environments.
When to Choose Aluminum Alloy 6061
Projects require excellent machinability and easy fabrication.
Cost is a primary concern, and budget constraints exist.
Applications involve moderate strength needs and good corrosion resistance.
The environment is less aggressive, such as indoor or atmospheric conditions.
Typical uses include aerospace components, construction profiles, and consumer goods.
When to Choose 6082 Aluminum Alloy
The project demands maximum strength and durability.
Exposure to harsh environments, such as marine or chemical settings, is expected.
Structural integrity and resistance to mechanical stress, wear, and deformation are critical.
Welded joints must maintain strength under load.
Heavy-duty transportation, bridge structures, and offshore platforms benefit from 6082’s properties.
Tip: For projects where overall mechanical performance is the top priority, 6082 aluminum alloy delivers superior results. For applications that value versatility and cost-effectiveness, aluminum alloy 6061 remains a reliable option.
Additional Considerations
Recent advancements in aluminum forging technology have improved both alloys. Aluminum alloy 6061 now offers excellent corrosion resistance and weldability, making it a strong candidate for aerospace and construction. 6082 aluminum alloy features high strength and good machinability, which suits transportation and heavy structural applications.
Environmental factors play a significant role. Aluminum alloy 6061 performs well in atmospheric conditions, while 6082 excels in marine and chemically aggressive environments.
Summary Table: Matching Alloy to Project Priorities
Project Priority | Recommended Alloy |
|---|---|
Maximum Strength | 6082 Aluminum Alloy |
Best Machinability | Aluminum Alloy 6061 |
Superior Corrosion Resistance | 6082 Aluminum Alloy |
Cost-Effectiveness | Aluminum Alloy 6061 |
Harsh Environments | 6082 Aluminum Alloy |
Versatility | Aluminum Alloy 6061 |
Engineers should review these guidelines and select the alloy that aligns with their project’s unique requirements. The right choice ensures optimal performance, durability, and value.
Aluminum alloy 6082 and aluminum 6082 t6 deliver improved strength and better corrosion resistance, especially for marine and outdoor use. Aluminum 6082 t6 suits heavy structural applications, while 6061 offers easier machinability and weldability for lightweight structures. The table below highlights their main differences:
Property | 6061 Aluminum | Aluminum alloy 6082 |
|---|---|---|
Strength | Lower | Higher |
Machinability | Easier | Harder |
Corrosion Resistance | Good | Better |
When choosing, consider these checklist items:
Property | Aluminum alloy 6082 | 6061 Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
Strength | High | Moderate |
Machinability | Moderate | High |
Weldability | Moderate | High |
Suppliers and experts recommend matching alloy properties to project needs. They advise evaluating exposure, required strength, and long-term maintenance. Consulting with professionals helps ensure the right choice for unique requirements.
FAQ
What makes 6082 aluminum alloy stronger than 6061?
6082 aluminum alloy contains more manganese, which refines the grain structure. This change increases strength and toughness. Many engineers select this aluminum alloy for heavy-duty applications where high strength is critical.
Is 6061 aluminum alloy easier to machine than 6082?
Yes, 6061 aluminum alloy offers better machinability. The lower hardness of this aluminum alloy allows for smoother cutting and shaping. Manufacturers often choose 6061 aluminum alloy for projects that require complex machining or tight tolerances.
How does corrosion resistance compare between these aluminum alloys?
6082 aluminum alloy provides better corrosion resistance, especially in marine or chemical environments. The combination of magnesium and manganese in this aluminum alloy protects against moisture and salt. 6061 aluminum alloy still resists corrosion but performs best in less aggressive settings.
What are the main uses for each aluminum alloy?
Engineers use 6082 aluminum alloy in bridges, cranes, and offshore platforms. This aluminum alloy works well for structural parts needing high strength. 6061 aluminum alloy appears in aerospace, automotive, and consumer products. Both aluminum alloys serve different industries based on their properties.
Why does the cost of 6082 aluminum alloy tend to be higher?
The cost of 6082 aluminum alloy is higher because of its increased strength and corrosion resistance. The alloying elements and production process add to the expense. Buyers often weigh the cost of 6082 against project requirements before making a selection.